The Link Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Breast Cancer
Scientific evidence mounts to support the idea that low vitamin D levels contribute to cancer growth.
| | Reading Time: 5 minutes

Scientific evidence mounts to support the idea that vitamin D deficiency contributes to cancer growth, and that optimizing vitamin D levels helps prevent cancer, and even improves chances of beating breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in American women, just behind skin cancers.
The American Cancer Society estimated that by the end of 2017, more than 252,000 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in the United States.
The Connection Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Cancer
In a 2012 study, researchers found that all women in the study group previously diagnosed with breast cancer were vitamin D deficient.
But, what about women with breast cancer who supplement with vitamin D? A study published in 2015 found that even in advanced stage breast cancer, women with high vitamin D levels lived longer than those with deficient levels.
Is there a vitamin D deficiency link with other cancers? A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that higher vitamin D levels improved survival in patients with follicular lymphoma. Additionally, researchers found the same results in other cancers, including colorectal, pancreatic, prostate, ovarian, and some types of lung cancer.
Is Sun Exposure Enough To Raise Vitamin D?
I’ve followed the epidemic of low vitamin D levels since 1984 when I taught clinical nutrition at the University of Humanistic Studies. Even in Southern California, my graduate students found that vitamin D levels were deficient. I became suspicious that sun exposure was but one way to get vitamin D, and that dietary sources were more important than sunlight.
My information research started with the premise that California surfers should make plenty of vitamin D and that their blood levels would be high. But, when I tested several surfers, all had vitamin D levels had varying degrees of low vitamin D levels. True, many surfers were vegetarians; they ate too many sugary foods and drank too many energy drinks.
Next, I tested patients from India, South America, Mexico, Hawaii, and Australia – all countries with high levels of sunlight— and found the same results: all had low or suboptimal vitamin D levels.
Then, research confirmed my clinical findings. A 2013 study in the United Arab Emirates found that vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency was prevalent in adolescents, particularly in girls. A 2015 study found vitamin D deficiency commonplace in Ethiopian children. Researchers found vitamin D deficiency is common in sunny countries worldwide including Australia, Thailand, and India.
An analysis of more than 13,000 vitamin D blood levels by Life Extension Foundation found that 87.5 percent had insufficient vitamin D levels. Vitamin D deficiency is a worldwide problem. It affects wealthy countries as well as developing nations.
With concerns about skin cancer risk and accelerated skin aging from overexposure to the sun, people were becoming shade lovers instead of sun worshippers. Applying sunscreen to block UV rays, also prevents vitamin D synthesis in the body. Although natural sunlight remains essential for health, food and supplements are necessary to optimize vitamin D levels.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is mainly found in animal foods. This biological fact makes it hard to get enough of the vitamin if you eat a vegan or strict vegetarian diet.
A 2013 study on vitamin D status in vegetarians found severe deficiency irrespective of sunlight exposure. Therefore, vegans may be at significant risk for a deficiency unless they consume vitamin D fortified soy and other vegetarian products. Another way to help boost vitamin D levels for vegans is to eat wild mushrooms or irradiated farmed mushrooms.
Highest Vitamin D Foods:
- Cod liver oil, one tablespoon 1,360 IU
- Swordfish, 3 ounces 566 IU
- Sockeye Salmon, 3 ounces 447 IU
- Tuna, canned 3 ounces 154 IU
- Sardines, two whole sardines 46 IU
- Beef liver, 3 ounces 42 IU
- Egg, one 41 IU
- Wild morel mushrooms, 3.5 ounces 212 IU
The only way to be sure you are getting enough vitamin D from your diet, or sunlight, is to get tested.
Test Your 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D Level
Vitamin D status is measured in the serum as 25-hydroxy vitamin D from a blood test. Because of its importance for health, many doctors now order a vitamin D test on routine blood screening. I order vitamin D testing on all my patients. You can order 25-hydroxy vitamin D on your own from Life Extension Foundation, Direct Labs, PersonaLabs, or Anytime labs.
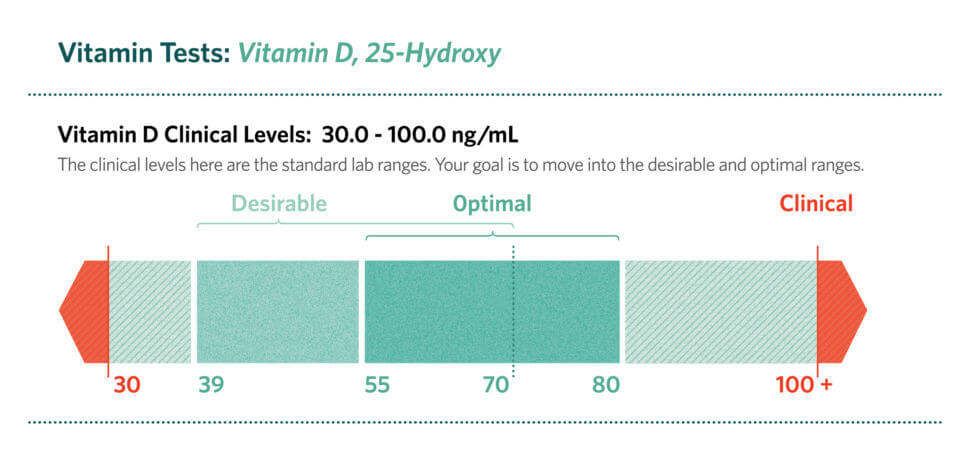
Vitamin D Levels from The Complete Blood Test Blueprint by Dr. J. E. Williams
Researchers hotly contest what level makes for optimal vitamin D in the body. For example, A 2016 study found that women over 55 years who have vitamin D of 40 ng/mL or higher had a 67 percent lower risk for all types of cancer. Some medical groups argue that over 50 is best.
However, to prevent cancer, heart disease, metabolic conditions, and slow aging, a 25-hydroxy vitamin D level between 55-80 ng/mL, and even up to 100 ng/mL is better. A 2008 report found that serum levels of at least 75 ng/mL are required for cancer prevention. An optimal level may be as high as 90-120 ng/mL.
But, more is not necessarily better. Levels above 125 may cause adverse effects, including the buildup of calcium in the blood. Vitamin D toxicity is rare, even among people who take vitamin D supplements. Symptoms include nausea and vomiting, weakness, and kidney complications.
Choose the Best Vitamin D Supplements
Sun exposure is not enough to increase your vitamin D level. The quickest solution to correcting low vitamin D is to get vitamin D3 injections. Secondly, the next best option is to take vitamin D3 supplements. But, don’t guess, get tested first.
However, not all vitamin D supplements are equal. Our bodies do not absorb many over-the-counter brands well enough. That is why I recommend pharmaceutical grade Vitamin D3 in capsules or liquid. Dosages range from 400 IU to 10,000 IU per capsule.
How Achieve Optimal Vitamin D Levels
To achieve optimal vitamin D levels, go at it from several angles. First, get enough daily sun exposure. Consume vitamin D rich foods. Takes supplements if your 25-hydroxy vitamin D level is low or below optimal. Choose your dosage based on your test results. Retest in three months.
Read my latest post on Low Vitamin D and COVID
Your Personalized Vitamin D3 Recommendations:
- If your 25-Hydroxy D levels are below 55, take 2,000 IUs daily
- For levels below 39, take 5,000 IUs daily
- If it’s below 30, you need 10,000 IUs daily
It takes time for vitamin D levels to improve. You won’t notice much change right away. Retest your 25-hydroxy vitamin D level in three months, and again at six months. Adjust your dosage based on the results.
Don’t Forget Vitamin K
If you take doses of vitamin D3 above 5,000 IU daily, remember to take vitamin K2. You need extra vitamin K to support calcium metabolism that vitamin D alone cannot do. These two nutrients have a synergistic activity for building healthy bones and improving cardiovascular health, and cancer prevention.
A 2015 study found that menaquinone-4 (the most common type of vitamin K2) had marked inhibitory effects on breast cancer cells. Vitamin K also protects against prostate, pancreatic, and hepatocellular cancers.
Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency is an ignored health epidemic. Everyone should be tested, starting in adolescents. If your vitamin D, 25-hydroxy level is below optimal, eat food high in vitamin D, get more sunlight, and take pharmaceutical grade vitamin D supplements.