The Age-Defying Effects of Spermidine: A Breakthrough in Anti-Aging Science
| | Reading Time: 9 minutes

We all want to be vital and maintain good health as we get older. But as you age, your cells undergo changes that can lead to reduced function, degenerative diseases, and accelerated aging. However, researchers found a natural compound that may help combat aging at the cellular level. Spermidine in foods like aged cheeses, mushrooms, and soy products appears to have life-extending effects. Wheat germ is exceptionally high in spermidine. Can spermidine supplements from wheat germ extract slow the effects of aging and improve wellness as we get older?
What Is Spermidine and Why Is It Important for Health and Longevity?
Spermidine plays an essential role in cellular functions. It is a polyamine compound found in all living cells, including plants and the human body’s cells, in minimal but critical amounts. Polyamines like spermidine are essential for cell growth and longevity. They contribute to the stability of RNA and DNA, nucleic acids that regular gene expression in health and disease, and aging. And they play essential roles in cell proliferation and survival.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek, the father of the microscope, discovered crystals in bull semen (sperm) in 1678; therefore, its name is spermine. But it wasn’t until the 1920s that scientists learned its chemical structure. Spermine derives from spermidine. The supplement form is spermidine.
Functions of the Polyamines Spermine and Spermidine:
- It helps regulate the immune response
- Cell signaling
- Cell structure
- Gene expression
- Cell proliferation and apoptosis
- Autophagia
As you age, polyamine metabolism falters, and spermidine levels decrease, contributing to rapid aging and increased incidence of age-related diseases.
Your body obtains spermidine in three ways: (1) from polyamine foods, (2) from the gut microbiome, and (3) from medical foods and nutritional supplements. Breast milk provides infants with abundant levels of spermine for growth and development.
In the body, spermidine helps maintain cellular homeostasis—the biological balance that sustains life. Studies show that spermidine may boost autophagy, the body’s ability to clear out toxic debris, including old and damaged cells. This process helps prevent untimely cell death and reduces inflammation, slowing or preventing age-related conditions.
Spermidine also influences pathways involved in aging and longevity. The MAPK pathway is one of those associated with modulating inflammation. Others involve autophagia and lipid metabolism. Research suggests that supplementing with spermidine may slow cellular aging and prolong lifespan.
What Exactly is Spermidine?
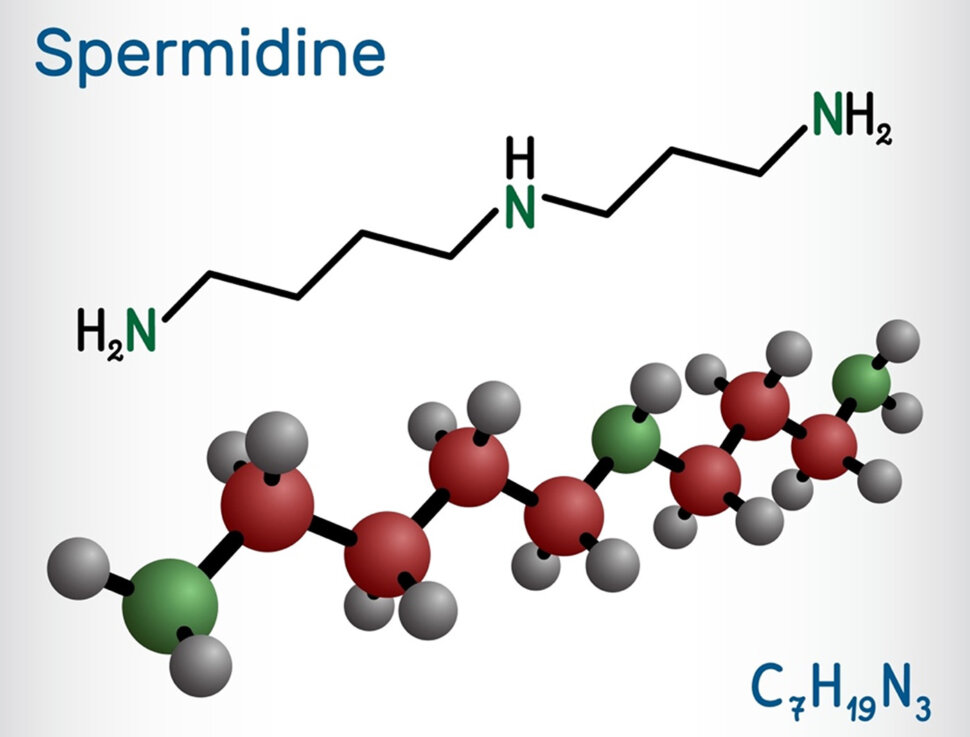
Spermidine is a triamine compound of three amines, synthesized in the body from ornithine and arginine, two amino acids common in many dietary proteins. It’s found within cells in ribosomes and has several essential metabolic functions. Spermidine is vital for proper cell function and replication. It is a fundamental metabolite, geroprotectant, and autophagy inducer. Studies show spermidine levels decline over a lifetime, contributing to aging and age-related disease.
How Does Spermidine Promote Anti-Aging and Longevity?
Spermidine has several anti-aging effects:
- It induces autophagy, a process where cells recycle waste material and damaged components. Autophagy declines with age, but spermidine restores autophagic function. In studies, spermidine extended the lifespan in model organisms by up to 30% through enhanced autophagy.
- It reduces inflammation and oxidative stress. Spermidine acts as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, helping prevent cell damage.
- It may improve memory and cognition. Spermidine has been shown to promote the growth of new neural connections in the brain and may help maintain memory and thinking skills as we age.
- It enhances mitochondrial function. Spermidine helps mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells, function optimally. The improved mitochondrial function provides more energy for cells and slows aging.
- It promotes cell proliferation and tissue regeneration. Spermidine stimulates stem cell proliferation and the growth of new cells to replace aging or damaged cells. This activity helps organs and tissues regenerate and stay healthy with age.
What Is Its Biological Significance?
Studies show that spermidine activates a process known as autophagy, helping clean out old and damaged cell components. Autophagia is essential for cellular health and longevity.
But autophagy declines with age, leading to cellular waste and the buildup of damaged cells. Spermidine helps maintain youthful levels of autophagy, which provides several benefits:
Promotes longevity. Studies in worms, fruit flies, and mice show that spermidine supplements can increase lifespan by up to 30%. In humans, higher spermidine levels promote longer lifespans.
Slows aging. Spermidine reduces many of the hallmarks of aging, like wrinkles, age spots, hair loss, and memory decline. It helps preserve muscle and bone mass while maintaining energy and vitality.
Fights disease. Enhanced autophagy helps remove the abnormal proteins associated with diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and certain cancers. Spermidine may reduce overall disease risk and slow the progression of common age-related conditions. However, too much spermidine may drive tumor growth in some cancers.
Improves memory. Spermidine supports the growth of new neural connections in the brain and protects existing connections. Studies show that spermidine supplements can reverse age-related memory loss and cognitive decline in just a few months.
Boosts heart health. Spermidine reduces inflammation, lowers blood pressure, and decreases plaque buildup in arteries. It helps maintain a healthy metabolism and body weight, supporting cardiovascular function.
Prevents neurodegenerative diseases. Preliminary research shows spermidine may even help in the fight against Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
How to Get Enough Polyamines Including Spermidine
There are three ways to maintain your body’s polyamine pool: (1) making enough in your body through natural biosynthesis, (2) in the gut microbiome by intestinal microorganisms, and (3) getting enough in your diet. A fourth way is by consuming spermidine superfoods and taking spermidine supplements.
Assure you eat enough polyamine foods, including green vegetables, mushrooms, and soy products. However, avoid foods that cause you allergies. Supporting gut health with prebiotics and probiotics like Lactoplantibacillus plantarum and eating LKM512 yogurt is beneficial. One of the best superfoods is wheat germ.
Wheat Germ: A Natural Spermidine Super Food
Wheat germ is a natural source of spermidine. This anti-aging compound may help slow down aging and prevent age-related diseases. As you age, spermidine levels decrease, so consuming foods high in spermidine, such as wheat germ, may help replace what is lost.
Nutritional Profile
Two tablespoons of wheat germ contain approximately 100 calories and provide a good source of plant-based protein with 5 grams. It is also high in fiber, B vitamins, vitamin E, folate, phosphorus, magnesium, and other minerals. The wheat kernel’s germ, a plant embryo, contains the highest nutrient concentration.
Wheat germ is not only one of the best sources of spermidine; it’s one of the original anti-aging foods. It contains 1.5 milligrams of spermidine per cup. Consuming spermidine-rich foods daily, such as wheat germ, may help slow the aging process by reducing cell damage and cell death and replacing old cells with new ones.
Health Benefits
In addition to being a source of spermidine, wheat germ phytosterols help support heart health, maintain healthy cholesterol levels, and enhance immune function. The B vitamins in wheat germ support healthy metabolism and stimulate the production of new cells. Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant to protect cells from oxidative damage. And the plant sterols found in wheat germ have cholesterol-lowering effects.
Adding just two tablespoons of wheat germ to your yogurt, oatmeal, smoothies, or baked goods a few times per week can provide these nutritional and anti-aging benefits. However, check with your doctor first, especially if you follow a gluten-free diet or have a wheat allergy. Wheat germ contains gluten. Avoid it if you’re gluten intolerant. When consumed in moderation, wheat germ can be a highly nutritious addition to your diet at any age.
Food Sources of Spermidine
Spermidine is in all foods, but some have more than others. The highest levels are in wheat germ and soybeans. The lowest in fruits. Excellent dietary sources of spermidine include:
- Mushrooms: Mushrooms are fungi that are rich in polyamines, like spermidine. Shiitake, oyster, and porcini mushrooms contain high amounts of spermidine. Eating more mushrooms is an easy way to boost your spermidine intake.
- Aged or fermented foods: As foods age or go through fermentation, the polyamine content increases. Foods like aged cheeses, natto, miso, tempeh, kimchi, sauerkraut, and sourdough bread are rich sources of spermidine due to the aging and fermentation processes used in their production. Include small amounts of fermented foods in your diet.
- Legumes: Legumes such as beans, lentils, and peas are high in spermidine. Soybeans and products made from soybeans, like tofu, edamame, and natto, are excellent sources. Adding more legumes to your diet through chili, hummus, and bean salads will increase spermidine consumption.
- Cruciferous vegetables: Cruciferous vegetables in the Brassica family, such as broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts, contain appreciable amounts of spermidine. You can eat them raw in salads or cooked by steaming, stir-frying, or roasting.
- Nuts: Most nuts, especially pistachios, almonds, walnuts, and pecans, provide a healthy dose of spermidine. Enjoy nuts as a snack, add them to yogurt or salads, or blend them into nut butter, sauces, and dressings. However, if you have allergies to nuts, skip them.
In summary, consuming foods naturally high in spermidine, such as mushrooms, aged cheeses, legumes, cruciferous vegetables, and nuts, may help boost your spermidine levels and promote longevity. Adding various spermidine-rich foods to your diet is the first step towards healthier aging and longer life.
Effects of Spermidine on Healthy Aging
As you age, taking a spermidine supplement can support healthy aging and longevity. You may get enough from foods and if you eat a lot of wheat germ. However, dietary sources alone don’t provide therapeutic levels to slow aging, so spermidine supplements have become popular.
Spermine trihydrochloride is considered the most biologically active form. It’s a molecule derived from wheat germ or rice-germ extract. But it’s not the same as spermidine. Its scientific designation is C10N26N4-4HCL. You may recall that spermidine’s designation is C7H19N3. Until we have more information, I advise avoiding the chemical version of spermidine.
Choose products that use concentrated wheat germ extract. For example, one spermidine company produces a 15:1 concentrated 1% spermidine supplement that provides 1 mg of spermidine in 3 capsules. Other products provide higher dosages.
Unfortunately, there’s yet to be a consensus on the best spermidine supplement! However, the research, and patient reports, are so favorable that I recommend starting a spermidine-enhanced diet, taking wheat germ, and adding a spermidine supplement.
Spermidine Daily Dosing
· Safe Daily Dose: 3 mg
· Upper Effective Dose: 6 mg
· Maximum Dose: 10 mg
Dosage and Safety
The typical therapeutic spermidine supplements dose is between 3-10 mg per serving, divided into two or three daily doses. It’s wise to start with the lower dose and gradually increase it to find what amount works best for you based on your health needs. Spermidine is considered safe for adults, with no known side effects or drug interactions at 3 mg.
As with any supplement, start with a low dose of spermidine, 1 mg twice or thrice daily with meals, slowly increasing to determine your ideal dosage up to 10 mg maximum. Before beginning a spermidine regimen, talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about interactions or side effects. Close medical monitoring may be needed for some individuals to ensure safety and efficacy.
However, as with any supplement, there are individual variations, so talk to your doctor before use, especially if you are on any medications.
Contraindications When Taking Spermidine
While spermidine shows significant promise as an anti-aging supplement, there are some contraindications before beginning a regimen.
Not only does it promote growth in the body, but it may also drive tumors. As we age, cancer becomes more common. Nature is wise. Perhaps the body reduces spermidine production to retard tumor growth. Though some researchers link lower spermidine levels during aging to increased cancer risk. The wise approach is not to take spermidine if you have or suspect cancer. Do not take high-dose spermidine supplements. Stay with the recommended doses.
Interactions With Medications
Spermidine may interact with certain medications by enhancing or inhibiting their effects. Spermidine could potentially impact the efficacy or potency of these drugs, including acyclovir, amantadine, choline, codeine, and others. Consult your doctor before taking spermidine if you are on long-term medications, especially for blood pressure, cholesterol, or diabetes management.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
There is little research on the effects of spermidine supplements in pregnant or breastfeeding women. However, breast milk is high in naturally occurring spermidine. Infant formulas are often supplemented with polyamines to mimic the spermidine concentration in breast milk. However, though spermidine supports growth during infancy, added polyamines alter the gut microbiome. Common sense is to avoid spermidine supplements during pregnancy and breastfeeding unless under the guidance of your doctor. But older mothers may benefit from taking spermidine.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
While spermidine is generally very well tolerated, some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, gas, or bloating, especially when starting supplementation. These side effects are usually temporary. Lower your dose to allow your body to adjust or switch to a delayed-release capsule.
Some have amine intolerance causing high histamine levels that trigger allergic reactions. These reactions can vary from migraine headaches to hives and gastrointestinal symptoms. You may react to high-spermidine foods like aged cheeses if you have amine intolerance.
High Blood Pressure
Spermidine may cause a slight, temporary increase in blood pressure due to its influence on nitric oxide levels and vascular function. People with uncontrolled or high blood pressure should use spermidine cautiously and under medical supervision. Daily 1 to 3 mg doses are recommended for those with high blood pressure.
Is There a Test for Spermidine Levels?
Blood or urine tests have yet to be widely available. Researchers have access to plasma levels in a blood sample. But your doctor cannot order a spermidine or spermine level from standard clinical reference laboratories like Labcorp, ARUP, or Quest Diagnostics.
Conclusion
In summary, spermidine is a natural compound with significant anti-aging effects that promotes longevity, slows aging, reduces disease risk, improves memory, and protects heart health. Supplementing with spermidine or consuming spermidine-rich foods are promising ways to achieve health and wellness into old age.
By making simple diet and lifestyle changes to increase spermidine levels, you have little to lose and potentially years of healthy life to gain. Though not a fountain of youth, getting enough spermidine is essential to age well. Staying abreast of the latest science, maintaining an open and skeptical mind, and consulting your doctor before changing your wellness routine will help ensure you make the right choices.
Spermidine supplements are also available. When taken at the proper dosage, it may help support longevity, heart health, brain health, and healthy aging. The quest for longevity continues, and spermidine offers an exciting new way to stay young.
Resources:
Gómez-Gallego C, Collado MC, Ilo T, Jaakkola UM, Bernal MJ, Periago MJ, Salminen S, Ros G, Frias R. Infant formula supplemented with polyamines alters the intestinal microbiota in neonatal BALB/cOlaHsd mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Nov;23(11):1508-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.10.003. Epub 2012 Mar 7. PMID: 22402370.
Madeo F, Bauer MA, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Kroemer G. Spermidine: a physiological autophagy inducer acting as an anti-aging vitamin in humans? Autophagy. 2019 Jan;15(1):165-168. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1530929. Epub 2018 Oct 11. PMID: 30306826; PMCID: PMC6287690.
Muñoz-Esparza NC, Latorre-Moratalla ML, Comas-Basté O, Toro-Funes N, Veciana-Nogués MT, Vidal-Carou MC. Polyamines in Food. Front Nutr. 2019 Jul 11;6:108. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00108. PMID: 31355206; PMCID: PMC6637774.
Nadège Minois; Molecular Basis of the ‘Anti-Aging’ Effect of Spermidine and Other Natural Polyamines – A Mini-Review. Gerontology Jun 1 2014; 60 (4): 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1159/000356748
Pegg, A. E. (2014). The function of spermine. IUBMB Life, 66(1), 8-18. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1237
Sagar NA, Tarafdar S, Agarwal S, Tarafdar A, Sharma S. Polyamines: Functions, Metabolism, and Role in Human Disease Management. Med Sci (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;9(2):44. doi: 10.3390/medsci9020044. PMID: 34207607; PMCID: PMC8293435.
Wortha, SM, Frenzel, S, Bahls, M, et al. Association of spermidine plasma levels with brain aging in a population-based study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023; 19: 1832–1840. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12815