Melatonin: What You Need To Know
| | Reading Time: 5 minutes

Melatonin is often called the “sleep hormone,”— but its benefits go far beyond just helping you fall asleep. From supporting your natural circadian rhythms to improving sleep disorders and boosting immune function, melatonin plays a key role in longevity and overall health. In this article, we’ll explore what melatonin is, how it works, and how to supplement it safely and effectively—, especially as you age.
What Is Melatonin and How Does It Work?
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland in the brain. Its release is triggered by darkness and signals the body that it’s time to wind down. As we age, our natural melatonin production declines, which may contribute to poor sleep and melatonin deficiency.
Supplementing with melatonin can help restore optimal levels and support healthier sleep patterns, particularly if you’re over 40 or experiencing chronic sleep disruptions.
What Are the Health Benefits of Taking Melatonin?
Melatonin has been extensively studied for its role in improving sleep, but its health benefits extend further:
- Helps manage jet lag symptoms
- Supports shift workers with irregular schedules
- Aids those with insomnia or circadian rhythm disorders
- Reduces anxiety before and after surgery
- May improve symptoms in some types of cancer patients
- Potential immune support, including in viral infections like COVID-19
- May improve mitochondrial health and cellular repair—important for longevity
Jet Lag
Melatonin can help reset your internal clock after long flights, reducing jet lag symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, and trouble sleeping.
Delayed Sleep-Wake Phase Disorder (DSWPD)
DSWPD causes individuals to fall asleep and wake much later than normal. Melatonin supplementation, when timed correctly, can shift your sleep cycle earlier and improve overall sleep quality.
Sleep Disorders in Children
Some studies suggest melatonin may help children with ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, or sleep-onset insomnia. However, always consult a pediatrician before giving melatonin to children.
Anxiety Before and After Surgery
Melatonin has mild sedative properties and may reduce preoperative anxiety and improve recovery time post-surgery, making it a gentle alternative to conventional sedatives.
Is Melatonin Helpful for Preventing or Treating COVID-19?
While melatonin is not a cure, some research indicates it may have anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects that support recovery from viral infections like COVID-19. More studies are needed, but it’s promising for supporting immune health in older adults.
Does Melatonin Help With Cancer Symptoms?
Emerging research shows that melatonin may help improve the quality of life for cancer patients by reducing fatigue, insomnia, and depression, especially during radiation or chemotherapy. It may also have antioxidant and anti-proliferative properties.
Can Melatonin Help With Insomnia?
Yes—melatonin is one of the most researched natural options for insomnia, especially in older adults. If you struggle with falling asleep, waking up too early, or poor sleep quality, you may have a melatonin deficiency. Supplementation can help reset your sleep cycle.
Does Melatonin Work for Shift Workers?
Shift workers face chronic disruption of circadian rhythms. Taking melatonin can help reduce daytime sleepiness and promote better sleep during off-hours, improving performance and mood.
Is It Safe to Take Melatonin?
Melatonin is generally considered safe when taken at recommended doses. However, like all supplements, it’s important to follow dosage guidelines and consider individual health conditions.
Interactions With Medicines
Melatonin may interact with:
- Blood pressure medications
- Blood thinners
- Antidepressants
- Immunosuppressants
Always consult your doctor before starting melatonin if you’re taking prescription medications.
Possible Allergic Reaction Risk
Though rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions like rash, itching, or shortness of breath.
Safety Concerns for Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Melatonin is not recommended during pregnancy or while breastfeeding unless prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Safety Concerns for Older People
Older adults may benefit the most from melatonin, but lower doses are typically recommended. High doses may cause morning grogginess or interact with medications.
Melatonin Is Regulated as a Dietary Supplement
In the U.S., melatonin is regulated as a dietary supplement, not a drug. This means:
- Products are not FDA-approved for safety or efficacy
- Labeling and dosing may vary widely between brands
Products May Not Contain What’s Listed on the Label
A 2017 study found that some melatonin supplements contained significantly more or less melatonin than stated. Always choose third-party tested products for purity and potency.
Is Melatonin Safe for Children?
While melatonin may help with specific pediatric sleep disorders, it’s not meant for general use in children. Dosage and safety should always be reviewed with a pediatrician.
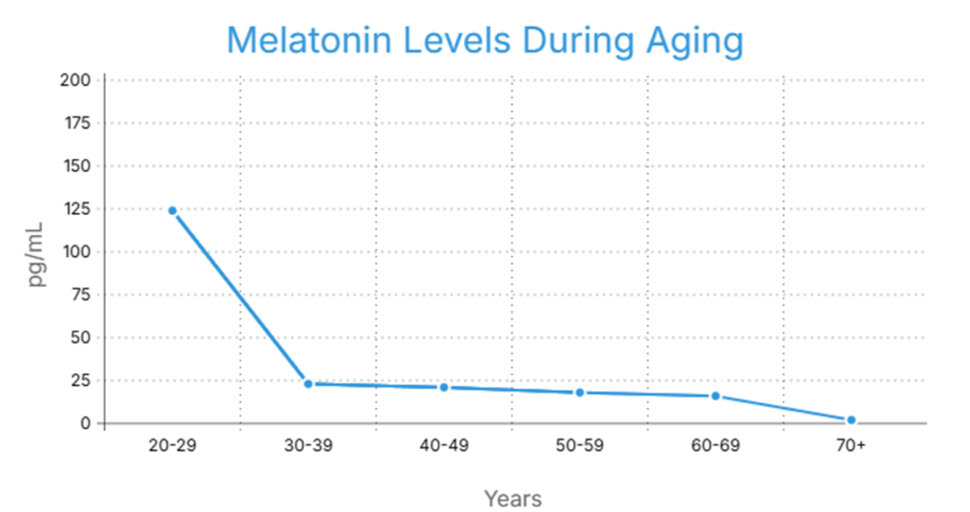
Melatonin Declines With Age: Why It Matters More Than You Think
Melatonin production follows a natural rhythm—high at night to promote sleep, low during the day to keep you alert. But what many people don’t realize is that melatonin levels drop sharply as we age. In fact, studies show that melatonin secretion peaks in early childhood, begins to decline in adolescence, and continues to decrease through adulthood. By the time you reach your 50s, levels can be significantly lower, and by age 80, melatonin may be almost undetectable in the bloodstream.
This decline contributes to common age-related sleep problems like insomnia, early waking, and lighter sleep. But more importantly, reduced melatonin levels have been linked to increased oxidative stress, lower immune resilience, and disrupted circadian rhythms—factors that can impact longevity and overall vitality. For adults over 40, supplementing melatonin may help restore this critical hormone’s natural rhythm, supporting not only restful sleep but also better mood, immune function, and long-term health.
What Are the Side Effects of Melatonin?
Common side effects include:
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vivid dreams
If side effects persist, lower the dose or discontinue use.
Tips To Consider
- Start low: Try 0.3–1 mg, then increase if needed. You can safely take 3-5 mg nightly if the lower doses aren’t sufficient.
- Time it right: Take 30–60 minutes before bedtime.
- Avoid high doses unless prescribed.
- Look for quality: Choose melatonin that’s third-party tested.
Consider body weight: Some research suggests dosing melatonin by weight may improve its effectiveness, especially in older adults.
How long does melatonin last?
What is melatonin tea?
What about melatonin patches?
Final Thoughts
Melatonin is one of the most powerful natural tools for enhancing sleep, restoring circadian balance, and supporting long-term health, especially as you age. If you’re experiencing sleep disruptions or want to support your longevity journey, consider high-quality melatonin supplements as part of your wellness routine.
Shop Now
Ready to take control of your sleep and health?
Explore Our Doctor-Recommended Melatonin Supplements →
Key References
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
- Sleep Foundation
- Mayo Clinic
- National Institutes of Health
- European Journal of Pharmacology
- Journal of Pineal Research