Do You Need a Gut Microbiome Test?
| | Reading Time: 5 minutes
Gut microbiome testing is a cornerstone diagnostic tool in functional medicine. It provides biological insights into the health or imbalances of your intestinal environment. Testing your gut microbiome is essential for lifelong health in today’s increasing occurrences of chronic diseases.
What Gut Tests Are Best?
I’ve ordered gut microbiome tests from patients’ stools for over thirty years. Back then, Genova Diagnostics was Great Smokies Laboratory. The lab in Ashville, North Carolina, pioneered functional medicine diagnostics.
Since then, microbiome science has evolved, and so has laboratory testing. Genova has an updated gut test called GI Effects.
Though I still use the GI Effects profile to gain a broad perspective of my patients’ intestinal microbiome health, my go-to stool test now is GI-MAP from Diagnostic Solutions.
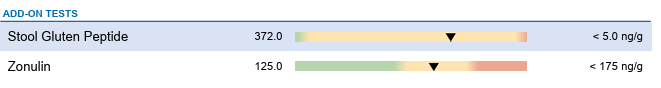
The GI-MAP (Microbial Assay Plus) is a comprehensive stool test that uses quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) technology to detect the presence of parasites, bacteria, H. pylori, fungi, probiotic organisms, and more by analyzing specific DNA signatures of organisms in the gut from a stool sample. In addition to microorganisms, it also measures particular health markers, like zonulin, that help detect a leaky gut.

The results provide a range of detected zonulin in a blood or stool sample to assess the integrity of the intestinal barrier. Zonulin is a protein with immune system roles that regulates the tight junctions in the small intestine to maintain the integrity of the gut lining. A high level indicates that molecules from the gut contents “leaked” into the bloodstream, triggering symptoms associated with functional conditions like chronic bloating due to IBS and in patients with autoimmune disorders and food intolerances.
Are Parasites Causing Your GI Symptoms?
A common myth is that parasites cause GI symptoms like bloating and frequent diarrhea. Of the many stool tests I’ve ordered, including ova and parasites stool studies from a standard medical lab like Quest Diagnostics, I found that modern Americans rarely have pathogenic parasites like Giardia, Cryptosporidium, or Entamoeba histolytica. These parasites cause prolonged diarrhea in travelers to countries where they are endemic, like developing nations in Africa, Asia, and Eastern Europe.
These organisms are not common in North America. Giardia does occur in the U.S., mainly in California. But it’s very uncommon, with an average of 6 cases per 100,000 people. Therefore, if you have chronic diarrhea, it’s unlikely to be caused by a pathogenic parasite.
However, get an ova and parasites study if you have GI symptoms, including watery diarrhea and cramping, and have recently returned from traveling to a third-world country. If your test is positive, your doctor will prescribe an antiprotozoal drug like metronidazole.
Natural anti-parasitic medicines include oregano oil, garlic extract, black walnut, and wormwood. However, in my clinical experience, these natural agents are less effective in eliminating an active parasitic infection than an antiprotozoal drug.
Chronic GI Inflammation
However, parasites are not the only cause of GI symptoms. Persistent inflammation is the leading cause of chronic abdominal symptoms, including diarrhea and bloating.
Many factors, including allergic and non-allergic sensitivities to foods, are the most common cause of GI inflammation. Viruses like Adenovirus and Norovirus can also cause chronic gut inflammation. However, these cases are common in immune-compromised patients, like those with B-cell immunodeficiency, not in typical chronic bloating.
Chronic gastrointestinal inflammation is called inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Symptoms include bloating and belly discomfort, diarrhea, or alternating constipation with diarrhea. Additional symptoms include joint pain, rashes, weight loss, and difficulty gaining weight, and patients often have urgent, explosive, loose stools. Severe cases are classified as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Should You Get Tested?
Consider microbiome stool testing if you have IBD or your symptoms persist for more than one month. And because chronic GI inflammation has become so common, I recommend a microbiome test as part of a comprehensive wellness clinical workup for all my patients.
Food allergy screening and gut immune studies, such as secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA) antibodies, should also be considered. SIgA is critical as a first responder in preventing infections caused by viruses and other pathogenic organisms, guarding against inflammation and autoimmunity. SIgA deficiency occurs in IBS, bacterial overgrowth, gastroenteritis, and autoimmune disorders.
Food sensitivities have become common. Food allergies involve the immune system’s response to the molecules in your food. Intolerances are not allergies but chemical reactions by the gut triggered by eating certain foods. People can develop intolerances to just about any food. That’s one reason I recommend rotating your foods every three days. Food allergies are immune cell-specific reactions. Tests for food allergies use IgE or IgG immunoglobulins.
Chronic GI symptoms are typically associated with IgG. For my patients, I start with the Food Specific IgG Allergy Panel from Quest. It tests for common foods like casein (found in milk), corn, eggs, wheat, and soy.
Besides food allergy testing, you may need a comprehensive gut microbiome analysis.
Order Microbiome Tests Without a Doctor’s Prescription
Some labs, like Diagnostic Solutions, require a licensed healthcare provider to order your test kit. The lab will drop-ship a test kit to a patient to conveniently collect their sample at home. I provide this service to my telehealth patients.
GI EFFECTS – Genova Diagnostics offers two levels of their test: (1) their standard test and (2) a premier option that includes the GI Effects panel plus Microbiomix, an enhanced microbiome report. The enhanced panel provides deeper biological insights for understanding your gut health.
VIOME – This at-home test kit checks for microorganisms in three tissue samples: stool, blood, and saliva. It also provides an estimate of your biological age. And it makes nutritional supplement recommendations. It’s like having a virtual functional medicine physician.
GUT HEALTH TEST—Thorne is a trusted professional company that provides clinical-grade supplements to healthcare practitioners. They emphasize personalized, science-driven wellness. This test measures the DNA of microorganisms in a stool sample.
ZOE—This research-based group of blood and stool tests provides insights into what to eat to stay healthy and live longer.

Restore Microbiome Balance and GI Immunity
Trillions of microorganisms live in the human intestinal tract. They comprise a complex ecosystem with essential roles in health and disease. Common keystone bacteria include lactobacterium, lactobacillus, and Akkermansia municiphila.
Dietary changes that can restore microbiome balance include eliminating refined sugar and carbohydrates, increasing fiber, staying hydrated by drinking pure water, and taking high-dose probiotics.
Professional-grade probiotics contain 10-50 billion CFU per capsule. You’ll need more than 300 billion CFU daily to rebalance the gut microbiome effectively.
Steps To Restore Microbiome Integrity:
- Make a list of your GI symptoms
- Note previous diagnoses and test results
- Get a GI-MAP or GI Effects stool test
- Find expert functional medical help to define what’s causing your symptoms
- Outline a treatment program, including dietary changes and natural supplements like probiotics
- Complete a follow-up microbiome study in 1-2 years.
Restoring gut health takes time. It involves dietary changes, including eliminating all ultra-refined and allergic foods. You’ll need adequate fiber and enough water to avoid overeating. Plan regular meals to optimize nutritional value. A microbiome test profile provides a map to guide your healthy journey of optimizing gut health.
Selected Resources
Fasano, A. (2012). Zonulin, regulation of tight junctions, and autoimmune diseases. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1258(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06538.x
Shanahan F, Ghosh TS, O’Toole PW. The Healthy Microbiome-What Is the Definition of a Healthy Gut Microbiome? Gastroenterology. 2021 Jan;160(2):483-494. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33253682/ Epub 2020 Nov 27. PMID: 33253682.
Smith, T., & Cunningham-Rundles, C. (2018). Primary B-Cell Immunodeficiencies. Human Immunology, 80(6), 351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2018.10.015